Assets
In Cognite Data Fusion, the asset resource type stores the digital representations of objects or groups of objects from the physical world, such as water pumps, heart rate monitors, machine rooms, and production lines.
About assets
Assets connect related data from different sources and are core to identifying all the data relevant to an entity (contextualization) in Cognite Data Fusion.
All other resource types, such as time series, events, and files, should be connected to at least one asset. You can connect each asset to many resources and resource types. For example, you can connect a pump asset to the time series that measures the pressure within the pump, to events that record maintenance operations, and to a file with a pump diagram.
Assets themselves are organized into asset hierarchies. For example, one asset can represent a water pump that's part of a larger subsystem asset on an oil platform asset.
At the top of each asset hierarchy is a root asset, for example, an oil platform. Each project can have several root assets, and all assets under the root asset must have a parent asset.
See the assets API documentation for more information about how to work with assets.
Structure an asset hierarchy
The example shows you how to structure the asset hierarchy for the fictional SYSTEM 11:
SYSTEM 11
└───Pump
│ └───Heating cable
└───Pump
Outlined in CSV format, the system looks like this:
| name | description | externalId | parentExternalId |
|---|---|---|---|
| SYSTEM 11 | Sea water system | SYSTEM_11 | |
| Pump | Main pump for system 11 | PUMP_A | SYSTEM_11 |
| Heating cable | Heating cable for pump A | HEATING_CABLE | PUMP_A |
| Pump | Backup pump for system 11 | PUMP_B | SYSTEM_11 |
You can post all assets in one request when you structure an asset hierarchy.
-
Post the following request:
POST /api/v1/projects/<project>/assets
Host: api.cognitedata.comWith this request body:
{
"items": [
{
"name": "SYSTEM 11",
"description": "Sea water system",
"externalId": "SYSTEM_11"
},
{
"name": "Pump",
"description": "Main pump for system 11",
"externalId": "PUMP_A",
"parentExternalId": "SYSTEM_11"
},
{
"name": "Pump",
"externalId": "Pump_B",
"description": "Backup pump for system 11",
"parentExternalId": "SYSTEM_11"
},
{
"name": "Heating cable",
"externalId": "HEATING_CABLE",
"description": "Heating cable for pump A",
"parentExternalId": "PUMP_A"
}
]
}The response body will look similar to this:
{
"items": [
{
"externalId": "SYSTEM_11",
"name": "SYSTEM 11",
"description": "Sea water system",
"metadata": {},
"id": 4181031623333192,
"createdTime": 1562764416913,
"lastUpdatedTime": 1562764416913,
"rootId": 4181031623333192
},
{
"externalId": "PUMP_A",
"name": "Pump",
"parentId": 4181031623333192,
"description": "Main pump for system 11",
"metadata": {},
"id": 2975365566518130,
"createdTime": 1562764416913,
"lastUpdatedTime": 1562764416913,
"rootId": 4181031623333192
},
{
"externalId": "Pump_B",
"name": "Pump",
"parentId": 4181031623333192,
"description": "Backup pump for system 11",
"metadata": {},
"id": 1366019363753734,
"createdTime": 1562764416913,
"lastUpdatedTime": 1562764416913,
"rootId": 4181031623333192
},
{
"externalId": "HEATING_CABLE",
"name": "Heating cable",
"parentId": 2975365566518130,
"description": "Heating cable for pump A",
"metadata": {},
"id": 3816457134628307,
"createdTime": 1562764416913,
"lastUpdatedTime": 1562764416913,
"rootId": 4181031623333192
}
]
}
In addition to externalId, you get a unique id field and value. References within CDF use that id, so parentExternalId is translated into that new unique identifier. Also, you have a new rootId field that gives you the id of the root asset.
Rate and Concurrency Limits
There are limits on the rate of requests (RPS) and the number of parallel requests. A request exceeding the limits will result in a 429 error response: Too Many Requests.
Define limits at both the API service and endpoint levels. Every request has a different budget due to the varying resource consumption. For example, there are two types of requests: CRUD (Create, Retrieve, Request ByIDs, Update, and Delete) and Analytical (List, Search, and Filter). CRUD requests are less resource-intensive than Analytical requests. Among all Analytical requests, Aggregates are the most resource-intensive, so they receive their request budget within the overall Analytical request budget.
The limits for the API service and its endpoints are shown in the diagram below. These limits are subject to change based on consumption patterns and resource availability over time. Changes to limits will be notified in the changelog.
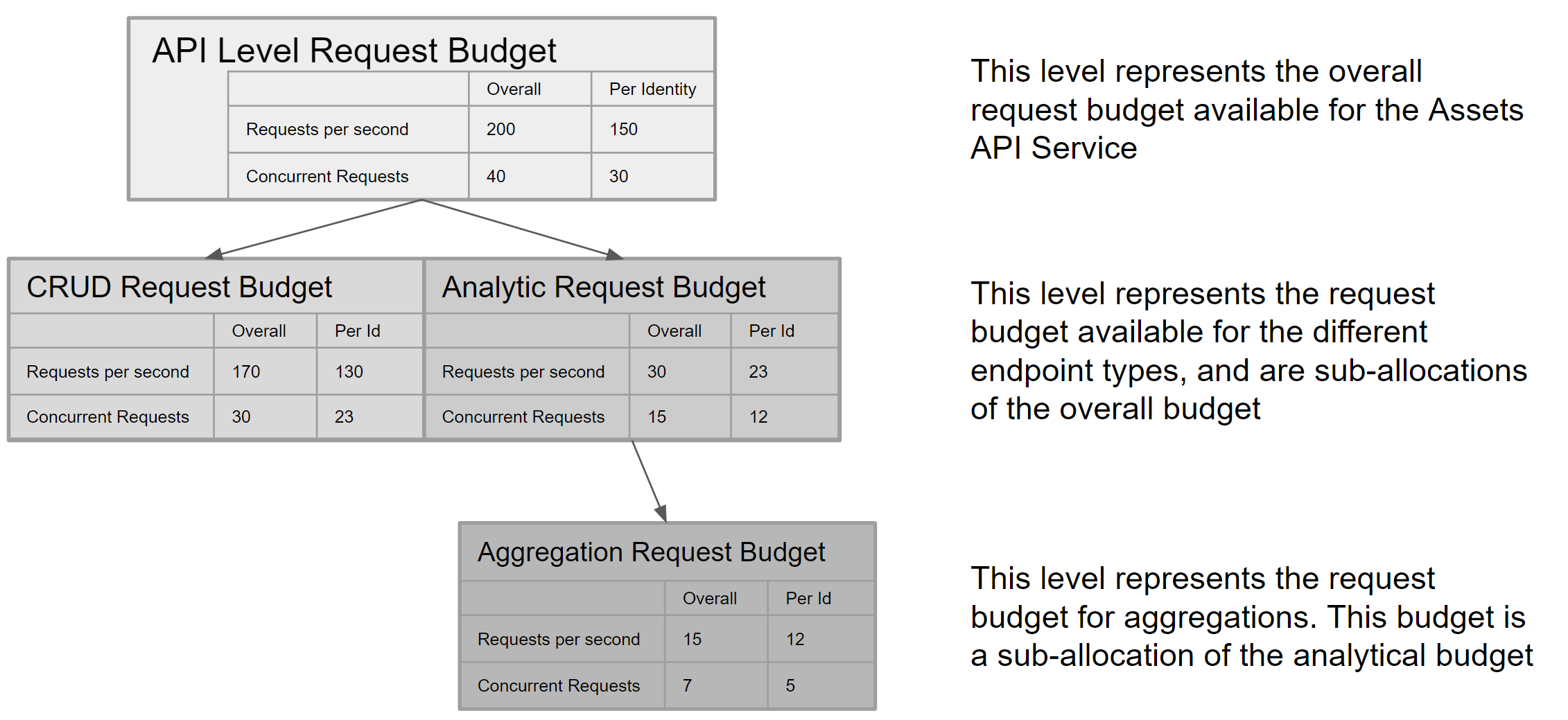
Translate RPS to data speed
A single request can retrieve up to 1000 items, where 1 item is an asset record. The top API service level has a maximum theoretical data speed of 200,000 items per second for all consumers and 150,000 for a single identity or client in a project.
Use of parallel retrieval
Parallel retrieval is a technique used to improve data retrieval performance in cases where due to query complexity, data retrieval speeds are lower than they would normally be with a fast, simple query. Use parallel retrieval to retrieve large data sets up to the capacity limits defined for an API service.
For example, the Assets API request has the following limits:
- A single request can retrieve up to 1000 items.
- Up to 23 requests per second may be issued for an analytical query (per identity), such as when using /list or /filter API endpoints (see above diagram).
Resulting in:
- A theoretical maximum of 23,000 items read per second per identity.
Additionally, complex analytical queries may return data slower than the theoretical maximum. Typically, the more complex the query, the slower the data rate.
Resulting in:
- A single request taking longer than 1s to read or write 1000 items.
Therefore, for complex 'analytical' queries that return data slower than the theoretical maximum, the query should retrieve fewer items per request and more in parallel until the theoretical maximum performance of 23,000 items per second is reached.
Use parallel retrieval only when a single request flow provides data retrieval speeds significantly less than the theoretical maximum. The overall requests per second limit still apply regardless of the number of concurrent requests issued. For example, if a request returns data at 18,000 items per second, adding a second parallel request provides little benefit as only 5,000 more items can be returned before the budget limit is reached.